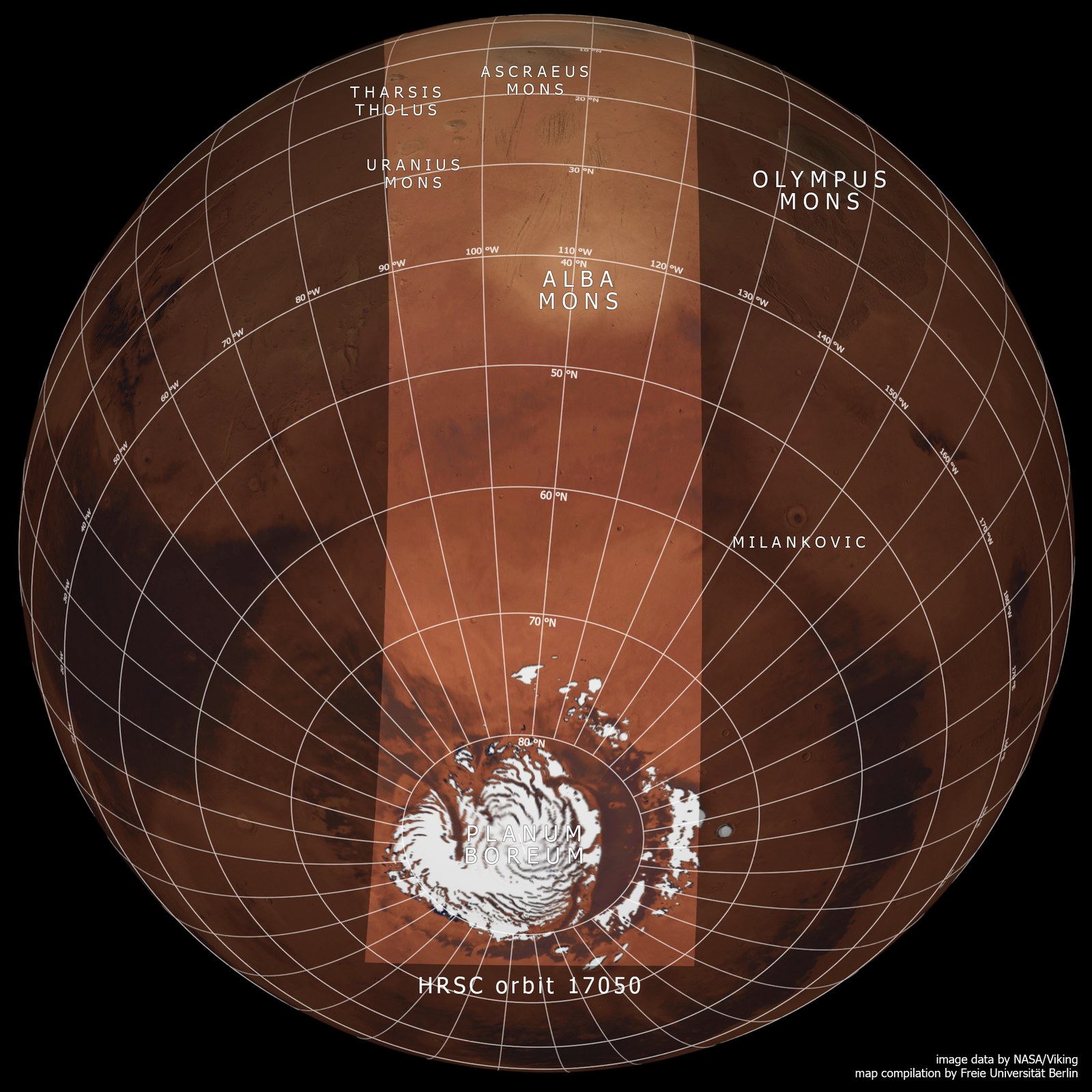
Mars upside down
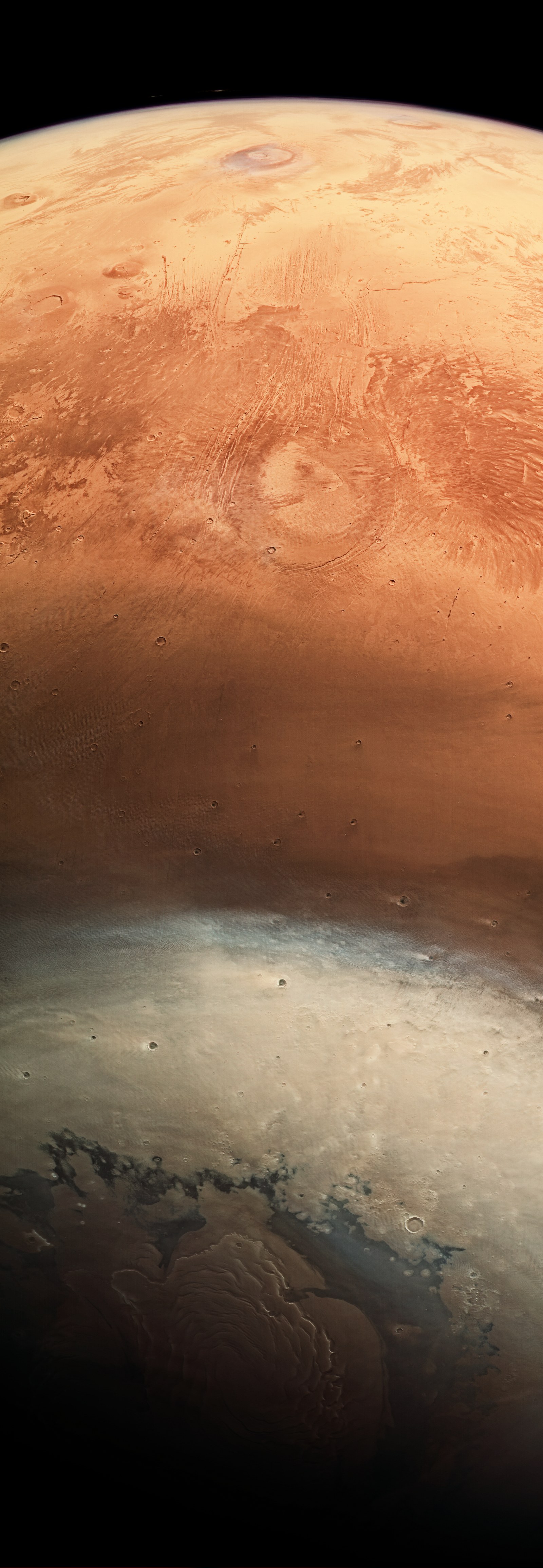
This unusual image, acquired by the Mars High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC), operated by the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) on board the ESA Mars Express spacecraft, shows a view of the northern hemisphere of Mars from the Martian north polar ice cap, situated at the bottom, up to the Martian equator at the horizon. It was taken for calibration of the camera on 19 June 2017. Calibrations must be repeatedly carried out during the course of the mission to guarantee the quality of the image data throughout the camera’s lifetime. The Mars Express spacecraft arrived at the Red Planet on 25 December 2003 – on the same day this year, the spacecraft will carry out orbits 17,698, 17,699 and 17,700 around Mars.
Readjustment of the camera system
Global views of planets are usually mapped with the North Pole at the top and the South Pole at the bottom – not the case in this HRSC image, taken from a high altitude when the Mars Express flew from north to south. Mars Express has a so-called polar orbit, which means that the spacecraft moves in elongated ellipses. With an inclination of 87 degrees with respect to the equator, these orbits pass almost directly over each pole, running from north to south, or from south to north over the planet. During each orbit, Mars Express approaches the surface to about 344 kilometres, and then moves away again to 8850 kilometres after the fly-by. The spacecraft orbits Mars every seven hours. Due to the position of the Sun when the image was acquired (spring in the northern hemisphere), the illuminated horizon is located close to the equator at the upper edge of the image, and the boundary between day and night, called the ‘terminator’ by astronomers (from the Latin 'Terminus', meaning border) is at the North Pole, which is why the ice cap at the lower edge of the image lies in shadow.
In this calibration picture, the sensors of the HRSC were directed over a wide extended area in a sweeping movement. That is why this type of recording is also called a 'broom calibration', because the field of view of the light-sensitive camera line sensors that are arranged perpendicular to the flight path are pushed across the surface like a broad brush stroke. In this way, all the sensors scan the surface at the same angle of observation, which is different from the usual configuration to systematically map Mars. The broom configuration is used for calibrating the individual sensors: in the case of the HRSC, these are four colour and stereo channels aimed forwards or backwards at an angle to the surface, and one nadir channel that is usually directed perpendicularly to the planet's surface, which obtains the highest resolution.
A rare view of Martian volcanoes
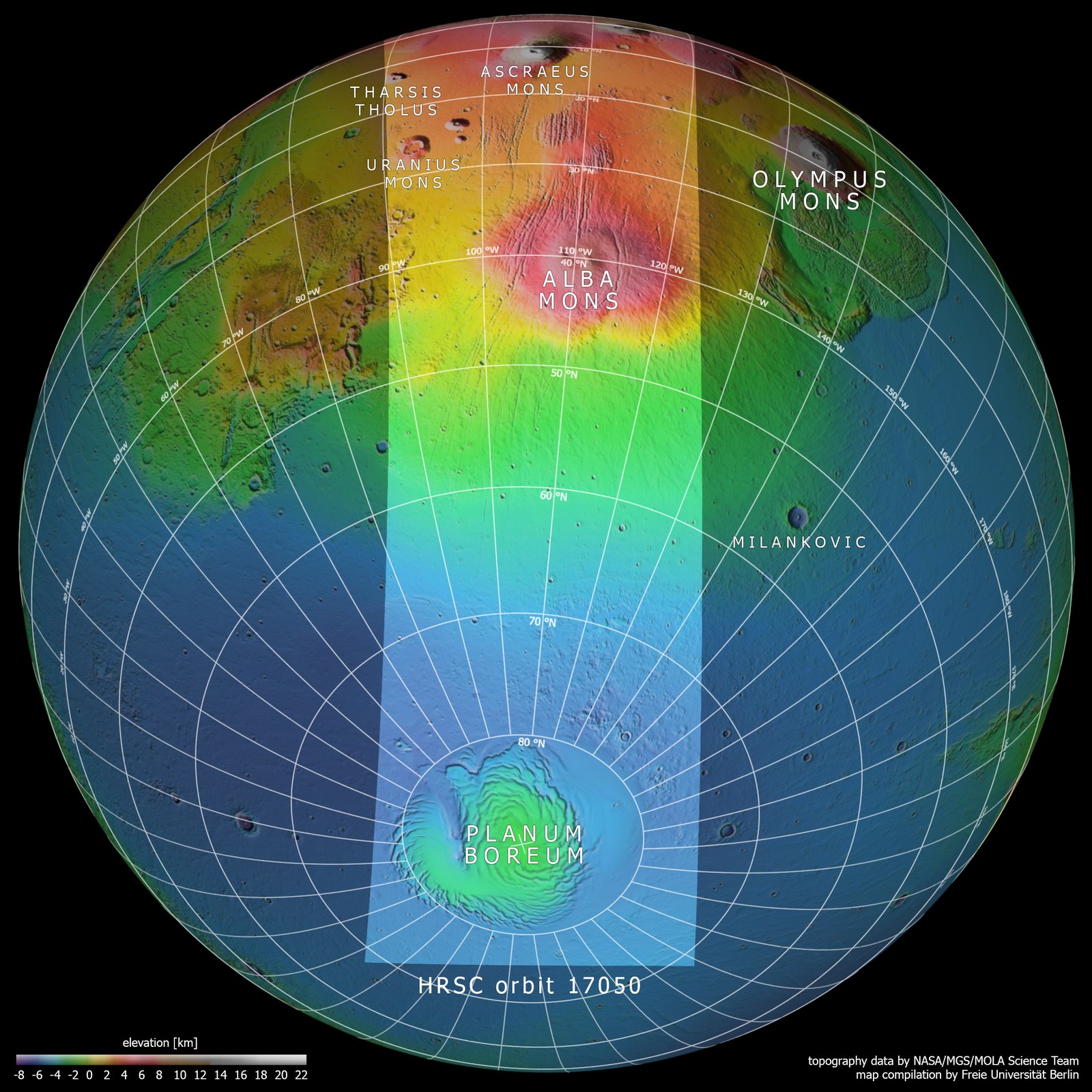
The wide angle of the image provides a rare look at several large Martian volcanoes in the Tharsis volcanic province, which rises up to five kilometres high like a mighty upward-curving shield the size of Europe. The production of heat and magma in Tharsis is probably related to one or more mantle plumes. In the past, the uprising mantle plumes and the high weight of the volcanic rocks on the Martian surface built up tension in the Martian crust. This produced numerous tectonic graben structures, faults and fissures in the Tharsis shield and in the peripheral zones of this region.
The volcano Alba Mons (from the Latin alba = white) can be seen as a white mark in the centre of the image, surrounded by tectonic faults. With a diameter of over 1000 kilometres, it is one of the largest volcanoes on Mars. The numerous graben running from south to north-east around Alba Mons were possibly created by subsidence of the Martian crust after discharge of a subsurface magma chamber, combined with crustal extension caused by the rise of the Tharsis shield.
Even the smaller volcanoes Uranius Mons, Ceraunius Tholus and Tharsis Tholus on the left-hand (eastern) edge of the image are still gigantic compared with those on Earth with diameters of over 100 kilometres and heights of several kilometres. Close to the horizon, the volcano Ascraeus Mons can be seen, 15 kilometres high and surrounded by hazy clouds of ice crystals. It extends over several hundred kilometres. Clouds at least 35 kilometres above the surface can be seen as thin streaks above the horizon.
Finally, the northern polar ice cap emerges from the shadows at the bottom of the image. This polar ice cap mainly consists of water ice and dust, but in this image it also features a broad ring of carbon dioxide ice (see also article northern polar ice cap 02/17 and 05/17). As the colour image was taken at the start of spring, the carbon dioxide ice produced in winter had not completely sublimated: it will change from a solid to a gaseous state and disappear into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas as the seasons progress. The volume of the permanent ice cap will then still be considerable at 1.2 million cubic kilometres, which corresponds to around one half of the Greenland ice cap.
Image processing
The images were acquired by the HRSC (High Resolution Stereo Camera) on 19 June 2017 during Mars Express Orbit 17,050. The image resolution is approximately one kilometer per picture element (pixel). The centre of the image is located at approximately 249 degrees east and 65 degrees north. The colour aerial view was created from the nadir channel, oriented perpendicular to the surface of Mars, and the colour channels of the HRSC. The maps of the region are based on data from the Viking mission and the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) experiments on board NASA’s Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) mission. Systematic processing of the camera data was carried out at the DLR Institute of Planetary Research. From this data, staff specialising in planetology and remote sensing at the Free University of Berlin produced the views shown here.
The HRSC experiment on board Mars Express
The High Resolution Stereo Camera was developed at the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) and built in collaboration with partners in industry (EADS Astrium, Lewicki Microelectronic GmbH and Jena-Optronik GmbH). The science team, which is headed by principal investigator (PI) Ralf Jaumann, consists of over 40 co-investigators from 33 institutions and 10 countries. The camera is operated by the DLR Institute of Planetary Research in Berlin-Adlershof. The camera has been delivering images of the Red Planet since 2004.