SpaceBot Camp

The DLR RMC (Robotics and Mechatronics Center – DLR RM and DLR SR) participated as team RMexplores! in den SpaceBot Camp Presentation on 13th of November 2015. The SpaceBot Camp was organized by the DLR Space Administration. Ten teams from universities and research institutes aimed at fulfilling a challenging task. A mobile system had to explore an unknwon area, find two objects and bring them to a third object for assembly. All tasks had to be done with a high level of autonomy since communication was delayed by 2 seconds and sending commands was limited to only a few occasions. The whole task had to be done in 60 minutes.
RMexplores! was the only team that fulfilled all tasks within the given specification. This was accomplished in halve of the time.

Your consent to the storage of data ('cookies') is required for the playback of this video on Youtube.com. You can view and change your current data storage settings at any time under privacy.
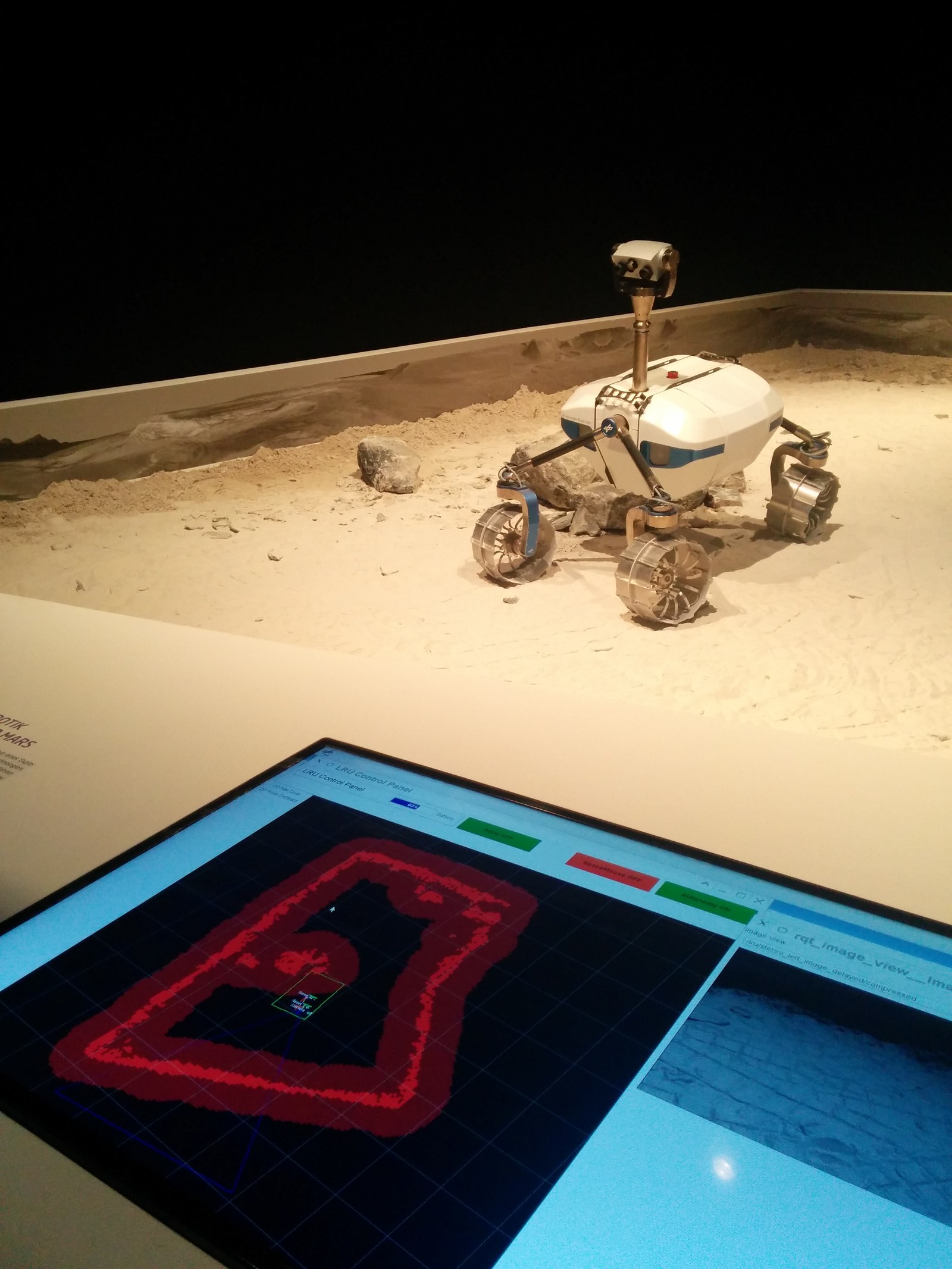

The used rover is called Lightweight Rover Unit (LRU). The system has been designed as breadboard for a lunar rover. The four wheeled system is highly maneouverable due to four independend steering and four driving motors. A robotic arm for manipulation is mounted on the back.
Three cameras on a pan/tilt unit are used as main perception sensors. Two of them are used as passive stereo cameras for navigation. The third one is a color camera for object detection. Another camera pair is mounted on the back and used for supporting manipulation with the robotic arm. An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) complements the sensors.

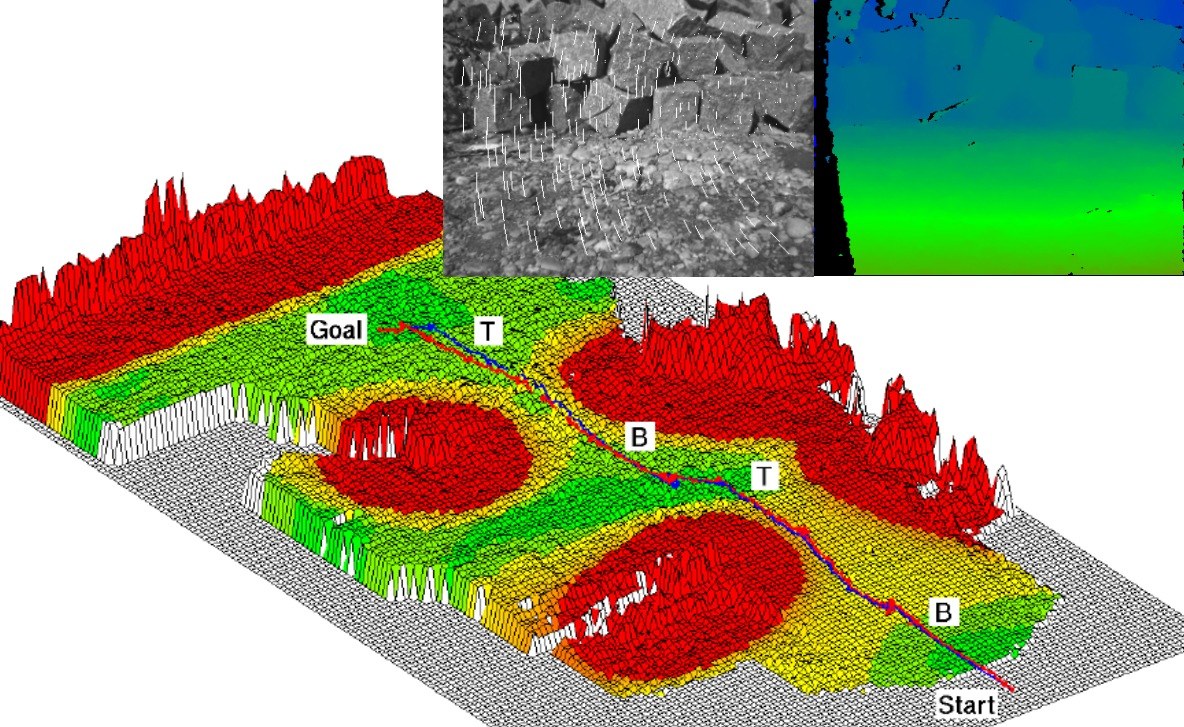
For environment perception, depth images are computed using the Semi-Global Matching (SGM) method. The stream of stereo images is also used for calculating visual odometry, which is fused with the data from the IMU. This provides the system with an accurate and robust ego-motion estimation. The depth image and ego-motion estimation are the base for mapping and path planning. The estimation of object location and orientation is based on the depth images and the an object fitting method.
More information is available on the German web page.