ROKVISS
ROKVISS aimed to provide a basis for new lightweight robot elements and to test and verify new robot hardware and powerful control concepts in realistic mission operation.
Runtime | 2005-03-22 to 2010-11-02 |
Project partners |
|
Acronym | Robotikkomponenten-Verifikation auf der ISS (ROKVISS) |
Fields of application | Space Robotics, designed for repair and assembly work in open space, Technology development for new lightweight robotic elements |
Project details
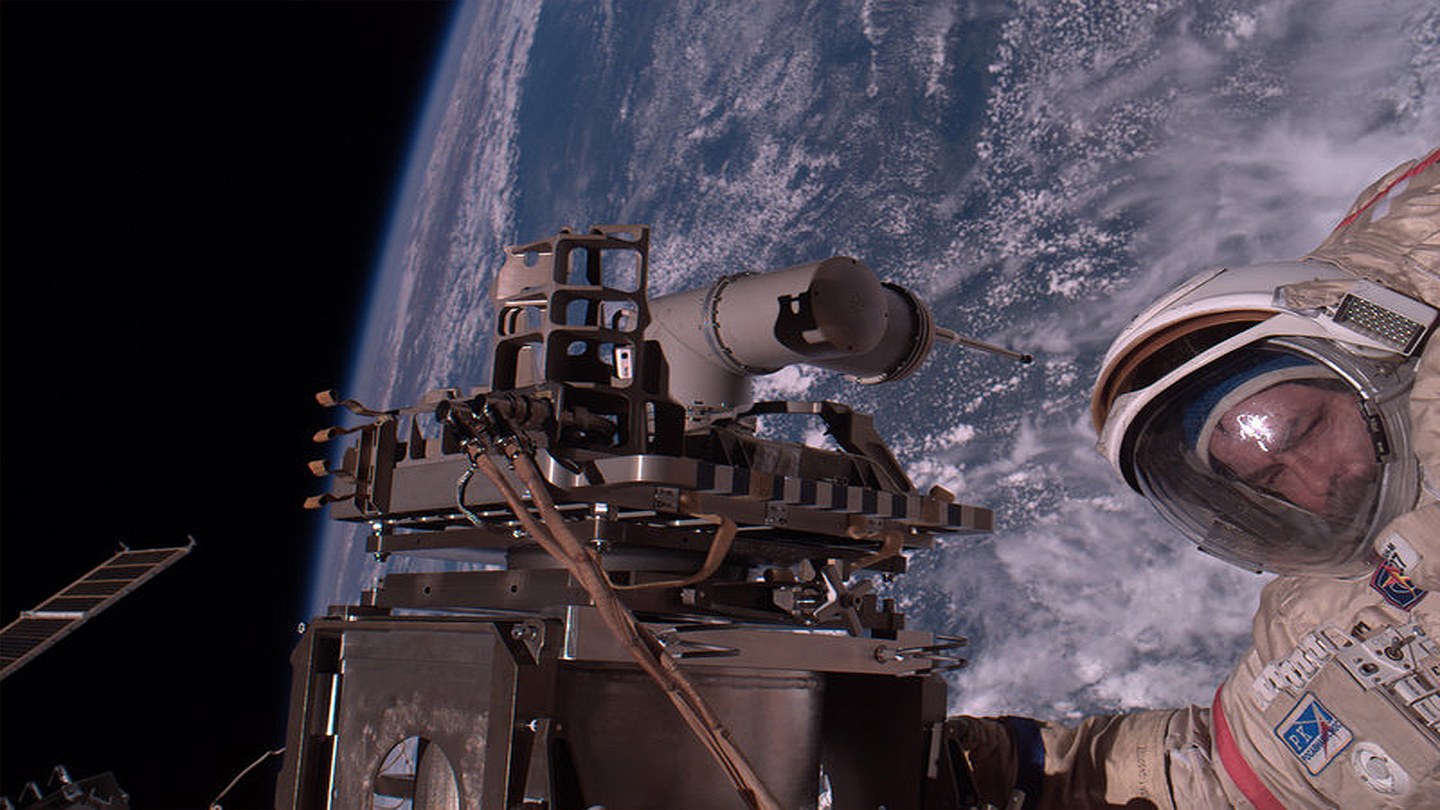
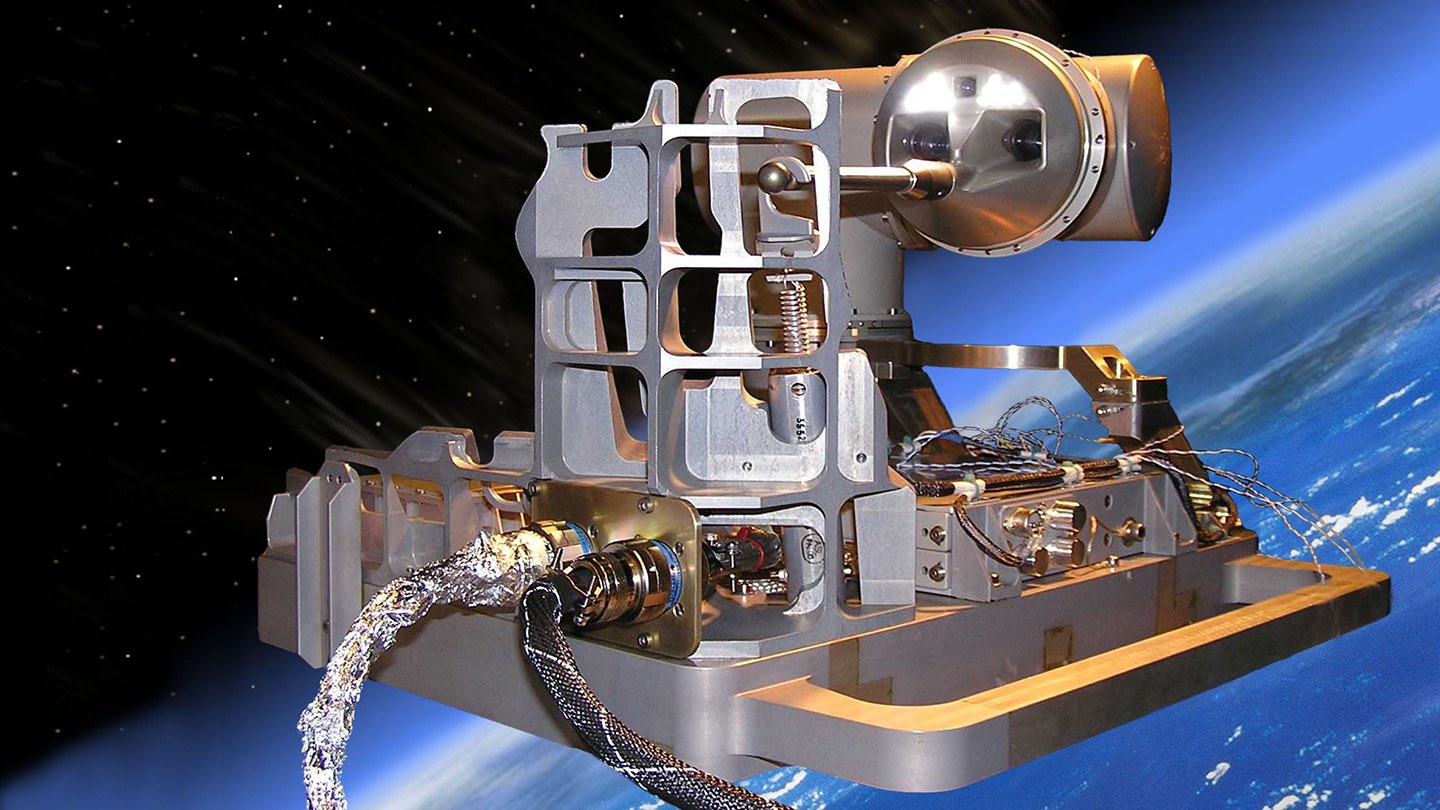
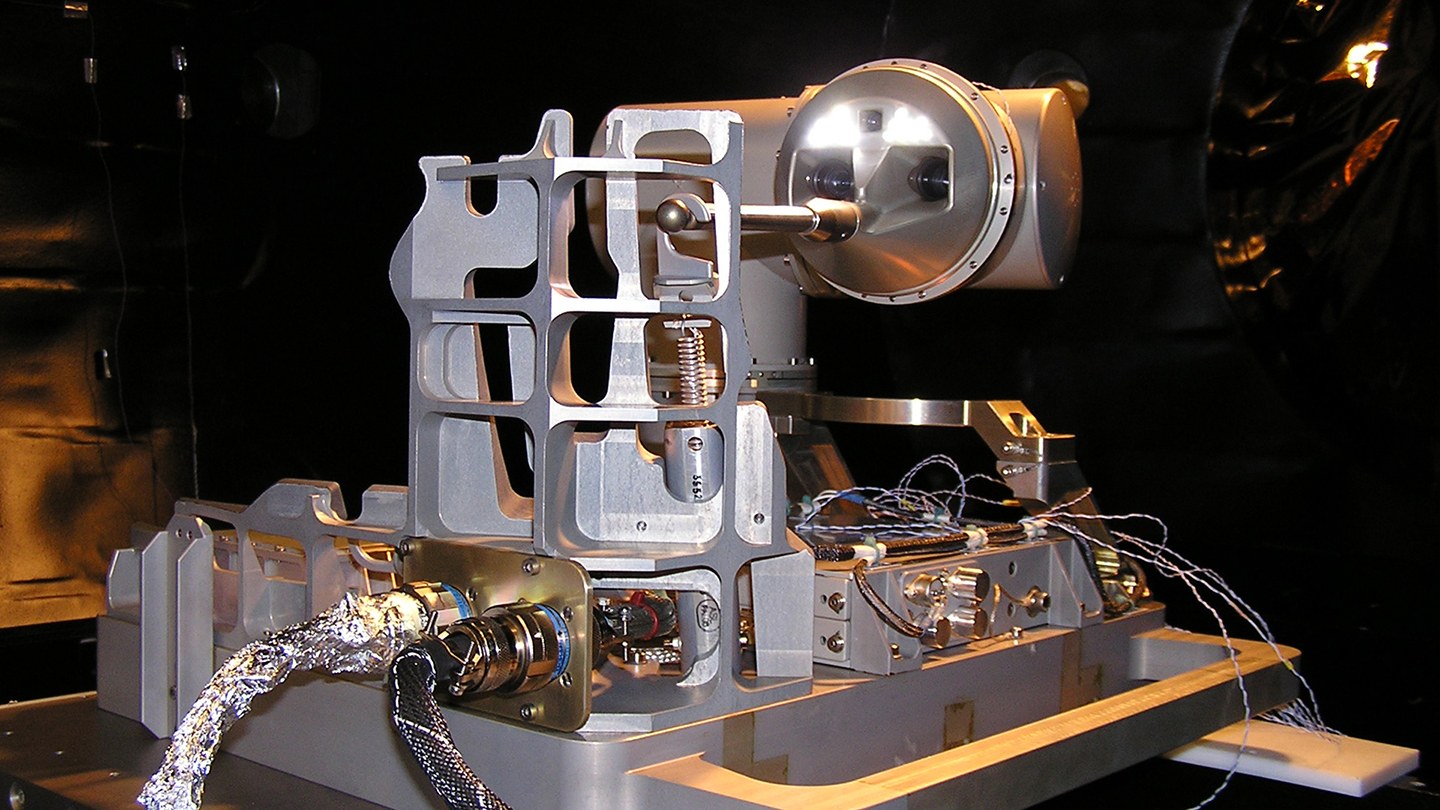
During its five and a half years of operation (2005-2010), the seven kilogram ROKVISS system completed over 500 tests in space. With its two joints, a metal finger and two integrated cameras, ROKVISS performed precise work in space.
For repair and maintenance work on satellites, the system has a tele-operation mode, giving the operator the feeling of doing the work directly at the remote location. During the overflight of the transmitting and receiving antenna in Weilheim (Southern Germany), the system could be remotely controlled directly from the ground in tele-presence mode. This was the first time that a robot in space was controlled from Earth without significant time delay - a novelty in space robotics.
For example, it was tested how precisely the robot arm can be controlled on the ISS using a joystick with so-called force feedback. The operator on the ground feels the force with which the robot presses against its environment in space. In addition, the engineers also investigated the energy ROKVISS absorbs during movement and how the friction of the bearings and gears behaves over long periods of operation in free space.
With the successful completion of this project, DLR has impressively underpinned its leading international position in the field of space robotics.
The costs for the ROKVISS experiment amounted to 11.5 million euros, including 3.5 million euros for launch, assembly and operation on the ISS, which was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF).