Fabry Perot Interferometer
The DLR-SO Fabry Perot Interferometer (SOFPIT) is an in-house development of the Institute for Solar-Terrestrial Physics at DLR that will measure thermospheric winds at an altitude of ~250 km. It makes use of an etalon (two reflective surfaces with a high degree of parallelism), for which the transmission is highly wavelength-dependent. This allows a precise measurement of the wavelength of airglow emission, and therefore the Doppler shift of the emitting population. For the SO-FPI, the observed airglow line is at 630 nm and comes from a layer of atomic oxygen at 200-300 km.
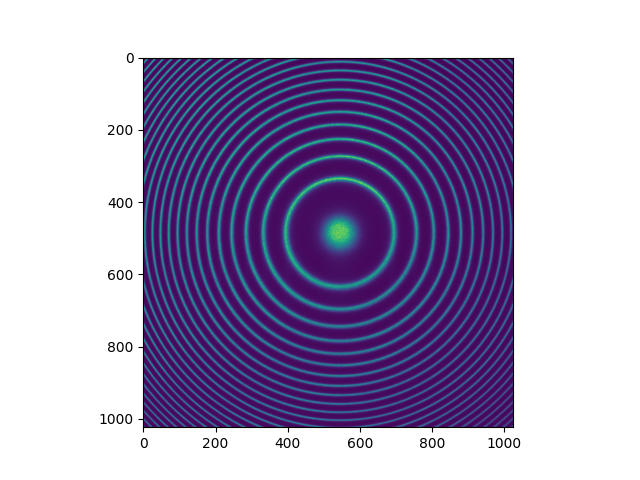
The raw data of the FPI consists of images of interference rings (see above, in false color). The diameter of the rings depends on the wavelength of the observed light, which in turn depends on the line-of-sight winds at the emission altitude. Similarly, the width of the interference fringes is dependent on the breadth of the emission spectrum and can therefore be used to derive an estimate of the thermal broadening of the emission line, thereby yielding an estimate of the temperature.
The FPI is installed in a climatized container so that it can be deployed to measurement locations. Its first deployment was conducted in early 2024, to Tenerife, Spain.