In the feasibility study, technological and operational requirements for the vehicle and refuelling and maintenance infrastructure were derived for various areas of use for shunting locomotives. The basis for the technical feasibility study of shunting locomotives in the German application context was a systematic survey of shunting locomotive operators.
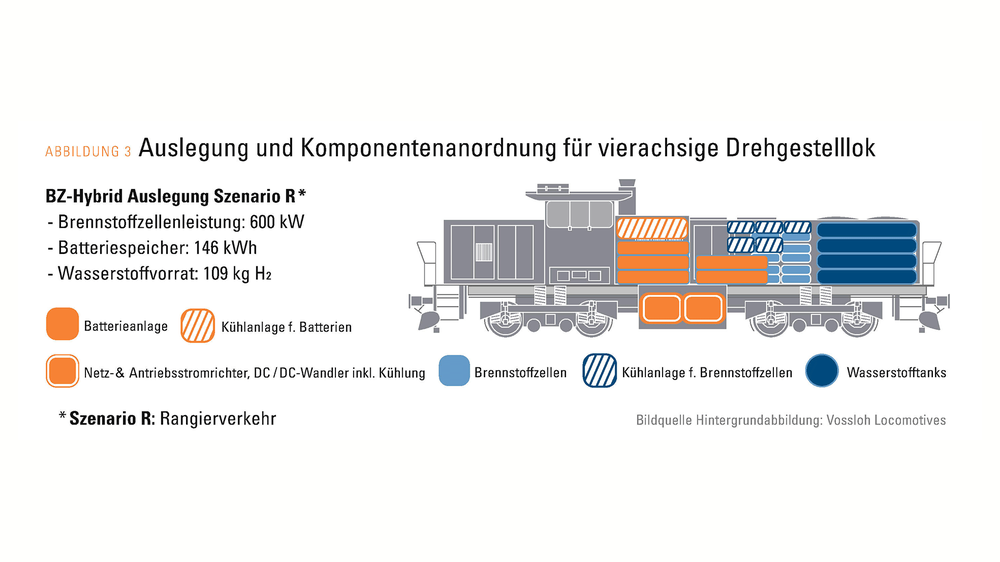
Based on the survey, characteristic load profiles were derived for the pure shunting service and the mixed shunting and line service (pure shunting profile, combined shunting and line profile and light delivery/operator travel profile). Simulation-based suitability analyses of various drive configurations were carried out on the basis of these load profiles. The pure battery drive, the fuel cell hybrid, the hydrogen combustion engine and the bi-mode variants battery overhead line hybrid and fuel cell overhead line hybrid were analysed. A widely used three-axle locomotive (Alstom Prima H3) and a four-axle shunting locomotive (MaK G 1206) were used as reference locomotives and the design and on-board arrangement of the required energy storage and converter components were carried out for these. Various charging concepts (charging while stationary, overhead line, etc.) were considered for the power supply of battery electric vehicles.
Following a presentation of the status quo with regard to completed and ongoing development projects for shunting locomotives with alternative drives, an assessment of their market potential in Germany was carried out in conjunction with the technical feasibility study. As part of this, the retrofitting of existing locomotives and the implementation in new vehicles were also analysed. Finally, potential obstacles to the use of shunting locomotives with alternative drives were identified and recommendations for action were made to industry and legislators.
Results
For the three-axle and four-axle shunting locomotive, it was shown that alternative drives for shunting locomotives are technically feasible under certain conditions. However, in order to be able to realise high trailing loads, especially in line operation, an adaptation or even a fundamental departure from current locomotive concepts is necessary. The main reasons for this are high performance and energy requirements combined with lower volumetric energy densities of alternative energy converter and energy storage components, which pose current and future challenges for integration into the existing installation space of diesel reference locomotives.
Project objective
- Survey of shunting locomotives in Germany
- Survey-based survey (shunting locomotive operators, railway undertakings) of the requirements for shunting locomotives with alternative drives
- Rough dimensioning of energy converters and storage systems based on characteristic load cycles for different shunting locomotive applications derived from the energy supply company survey
- Cost estimation and projection of market potential for alternative drives
Results
The results brochure with the key findings was published in March 2022:
Client
- NOW GmbH (Nationale Organisation Wasserstoff- und Brennstoffzellentechnologie)
Project duration
- 10/2020 until 10/2021

