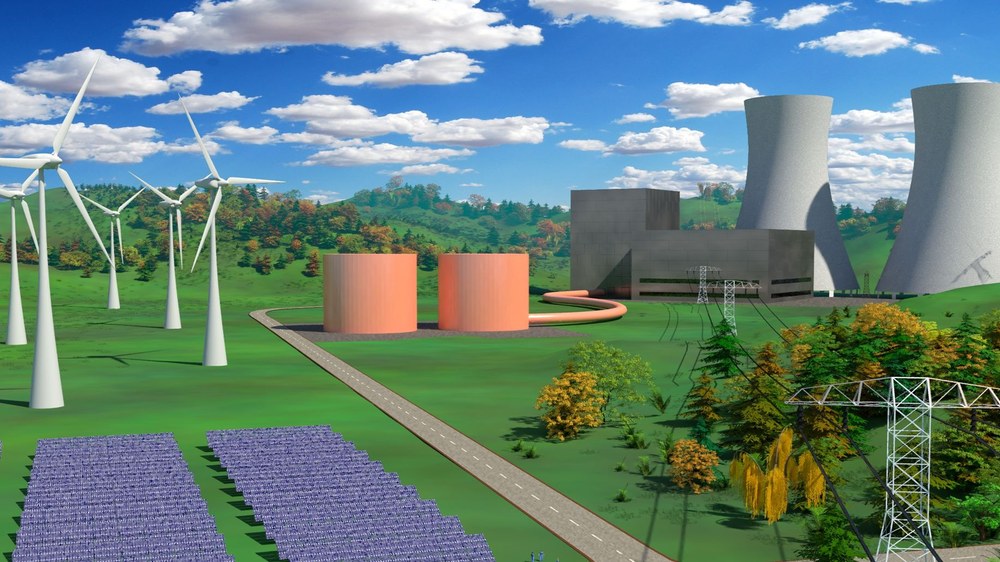
The institute develops application concepts for heat storage systems, particularly for industrial environments. The heat storage system acts as a buffer between the actual energy source and the consumer. Both concentrating solar thermal systems and electricity can be used to charge the storage tank. The storage medium liquid salt, water or solid can be heated up to 1,000 degrees Celsius depending on the application. Cost-effective energy storage can be realised through high temperature spreads in the storage unit. The heat accumulators themselves are being developed at the DLR-Institute of Engineering Thermodynamics.
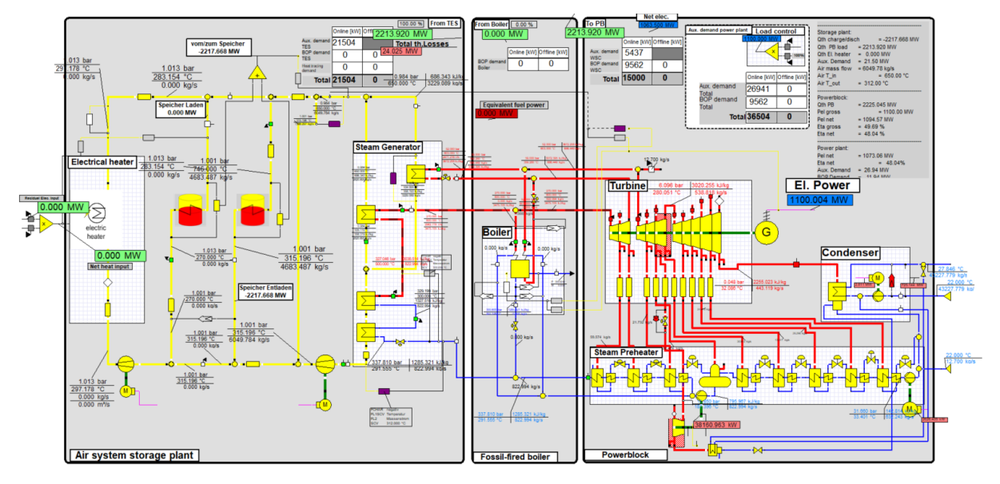
At the Institute of Solar Research, the system integration of the storage units is being technically developed and economically evaluated. The Sustainable Systems Process Engineering department uses the EBSILONProfessional software to create thermal circuit diagrams for complex systems. Depending on the application, different advantages of using storage tanks come into play. Primarily, it allows the temporal decoupling of energy consumption and energy supply. This makes it possible to optimise the electrical connected load and, with variable electricity prices, to procure energy at minimum cost. In addition, the storage system provides robustness against short-term power grid failures in sensitive applications.
Dynamic modelling and operational optimisation
For the respective application, the Institute of Solar Research analyses the operation of the storage system with the connected system components typically over one or more years. Only with this time-resolved analysis can the interaction between the storage system, energy sources and load be evaluated technically and economically. The system modelling working group has specialised simulation tools for annual yield calculations in time steps of 1 to 60 minutes. The focus of the work is on the detailed modelling of all processes relevant to the evaluation. In addition to the actual efficiencies, these are in particular transient processes such as start-up and shut-down of the individual system components. In the case of volatile energy sources and loads, operational optimisation is used, taking predictions into account.
Carnot batteries and heat storage power plants
Carnot batteries, also known as heat storage power stations, are power-to-heat-to-power systems in which a heat storage tank is charged with electricity. The heat from the storage tank is converted back into electricity via a heat/power machine. The system is therefore able to draw electrical energy at favourable times and supply it as required in the form of electrical power. It is advantageous to operate these systems with combined heat and power generation. Simple concepts such as loading a salt storage tank using an electric heater and reconversion with a steam turbine cycle achieve conversion efficiencies of up to 45 percent. The efficiency increases if the charging and discharging process and storage system are more closely integrated. Such systems are more complex and therefore more expensive. The Institute develops Carnot battery concepts for various applications, both with electric heaters and with high-temperature heat pumps. Here too, our focus is on detailed modelling, design, yield calculation and profitability analysis.
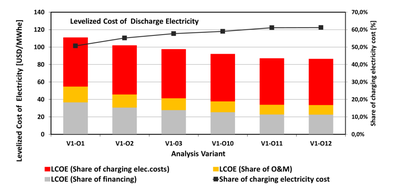
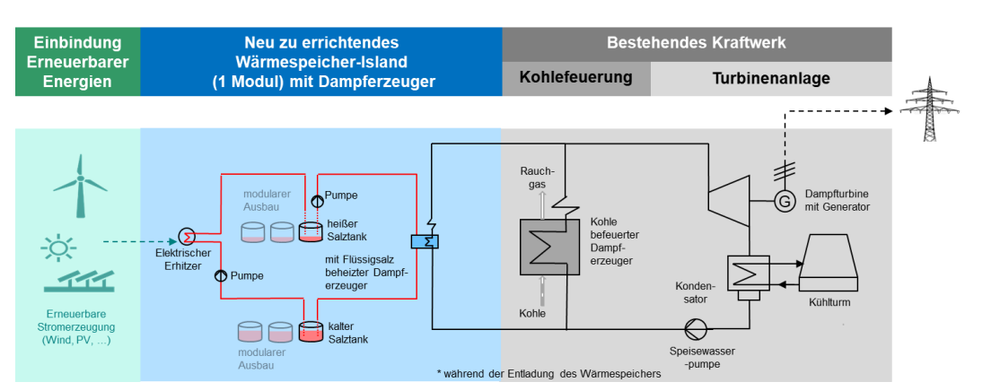
Conversion of coal-fired power plants into Carnot batteries
One interesting option is the conversion of existing coal-fired power plants into Carnot batteries. The existing steam turbine cycle is expanded to include a heat storage unit and the necessary charging unit. By using renewable electricity either from the grid or from its own generation via a PV system, the Carnot battery supplies green electricity as required. The existing coal-fired boiler can optionally be kept in reserve for secure energy generation or replaced by a boiler using more environmentally friendly fuels such as natural gas, hydrogen, biomass, etc. The analyses show that these systems are economical as soon as there is a sufficiently large spread in the electricity purchase price throughout the day. The Institute is working closely on this concept with the DLR-Institute of Engineering Thermodynamics and the DLR-Institute of Low Carbon Industrial Processes.
The work is generally carried out in close coordination with industrial partners who are either customers, component suppliers or system integrators.
From concept to demo plant
The Institute's research work ranges from initial concept studies to support for demonstration plants. The work is usually carried out in R&D projects together with industrial partners who define the respective application or act as system suppliers. In recent years, for example, numerous studies have been carried out on the conversion of coal-fired power stations.