Antarctic Ozone Hole has reached maximum size for this year’s (2010) season
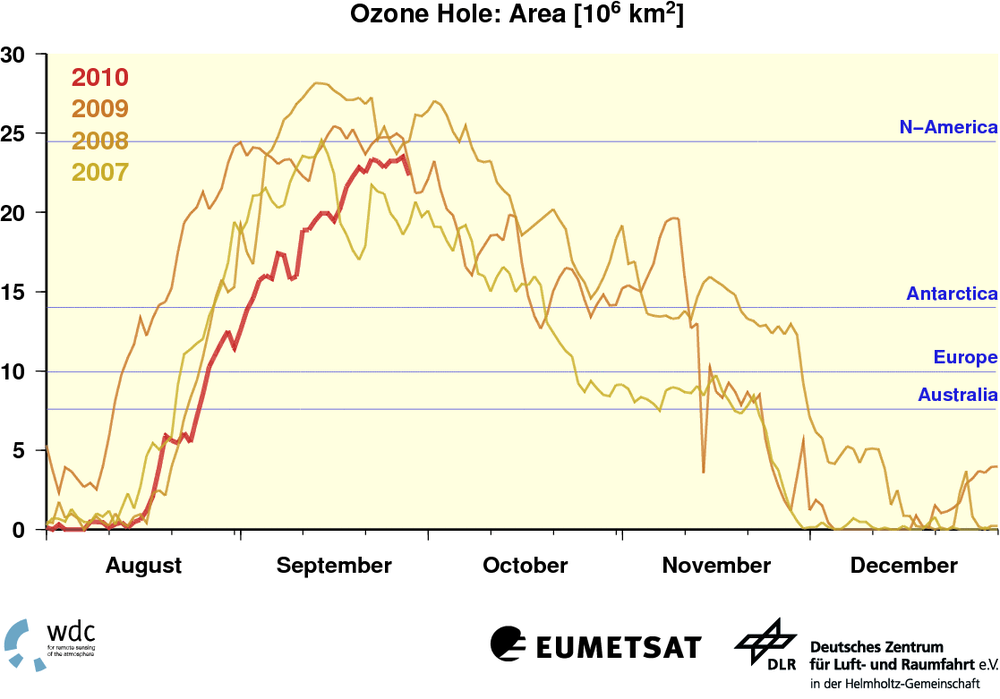
The Antarctic ozone hole has become prominent during recent years. Due to complex chemical processes ozone is being destroyed always with the advent of the first solar illumination in southern polar latitudes. This year is no exception. It is these days that the area of reduced ozone coverage reaches the maximum expansion within this year (2010): the ozone hole covers almost 23 billion square kilometres – this is equivalent to nearly the size of North America. It is expected that the ozone hole area now starts to shrink until its total recovery by the end of this year.
Satellite based measurements of the planet’s ozone distribution are being conducted in a routine manner from European space crafts since about 1995 when ENVISAT – the largest environmental satellite ever – was put into orbit. Today, the GOME-2 instrument on board of Europe’s spacecraft Metop-A continuously provides ozone data around the globe. The data are being assimilated at DFD into complex so-called Chemical-Transport Models to derive a comprehensive picture of the ozone distribution.
