MaTiC-M
Methods and Technologies for an intelligent Circularity of Materials
Closing material cycles is one of the pillars of the European Green Deal for tackling the energy transition. Sustainable – or, more precisely, recyclable – products are of utmost importance, as 80 percent of negative environmental impacts are caused in the design phase. However, manufacturers are usually not involved in the recycling and disposal of their own products. Without considering end-of-life recycling options, product designs always fall short of their recycling potential. To make the transition from low-quality mixed scrap and thermal recycling to high-purity secondary raw materials and increased material recycling, end-of-life must be taken into account when designing a product. New regulations and laws, such as the amended Ecodesign Regulation, are placing greater responsibility on manufacturers. The aim is to create products that can easily be repaired, reused, and recycled at the end of their life. This raises the question of how a product designer without extensive knowledge of material recycling can make efficient, sustainable design decisions. Until now, this has not been necessary, and to make things even more complicated, the necessary knowledge is spread across the recycling industry, even for a seemingly simple product such as a refrigerator.
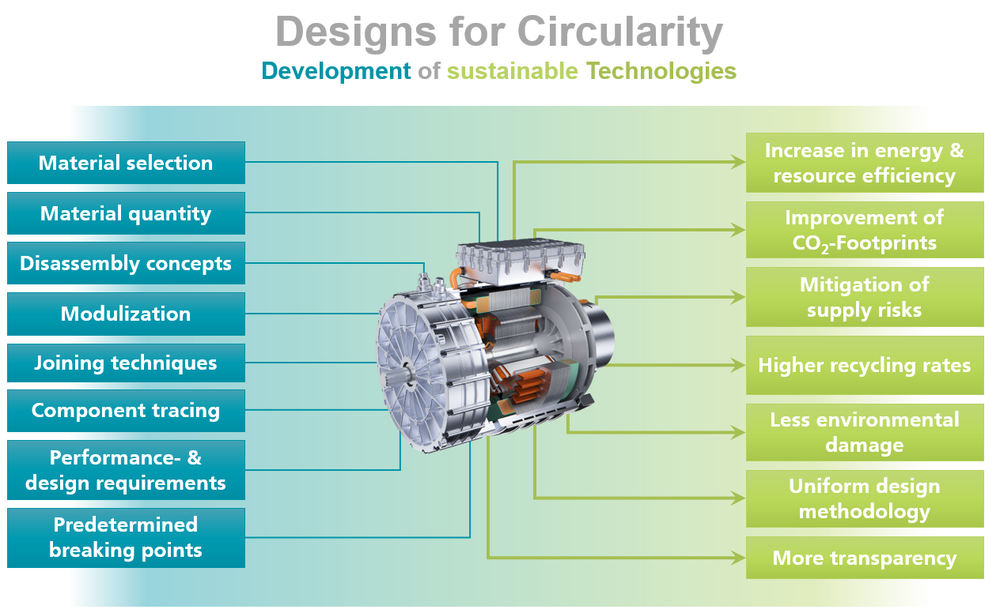
The MaTiC-M project seeks to close this knowledge gap between product development and recycling. The goal is to develop a software, the Design for Circularity Tool, to provide product designers with recommendations for improving recyclability, reducing supply-critical materials, life cycle costs, and carbon footprint. It is based on a new optimization approach, extensive data on secondary raw materials, and symbolic AI. The basic methodology consists of anticipating the recycling paths of each component and material, from disassembly, sorting, and processing to the production of marketable secondary raw materials.
Design decisions are made based on maximizing the Design for Circularity Score, which is composed of recyclability, criticality, costs, and carbon footprint. In addition, manufacturers can set their own priorities by adjusting the impact that each of the four parameters has on the Design for Circularity Score. Methodology and tool are being developed in MaTiC‑M based on four DLR technologies from the fields of aviation, energy, and transportation, for which DLR itself acts as the product developer. An industry advisory board of renowned companies from the field of mechanical engineering assists in preparing the tool for technology transfer. The transfer will be realised in follow-up projects and in direct cooperation with industry.
Project concept:

Design-for-Circularity-Tool
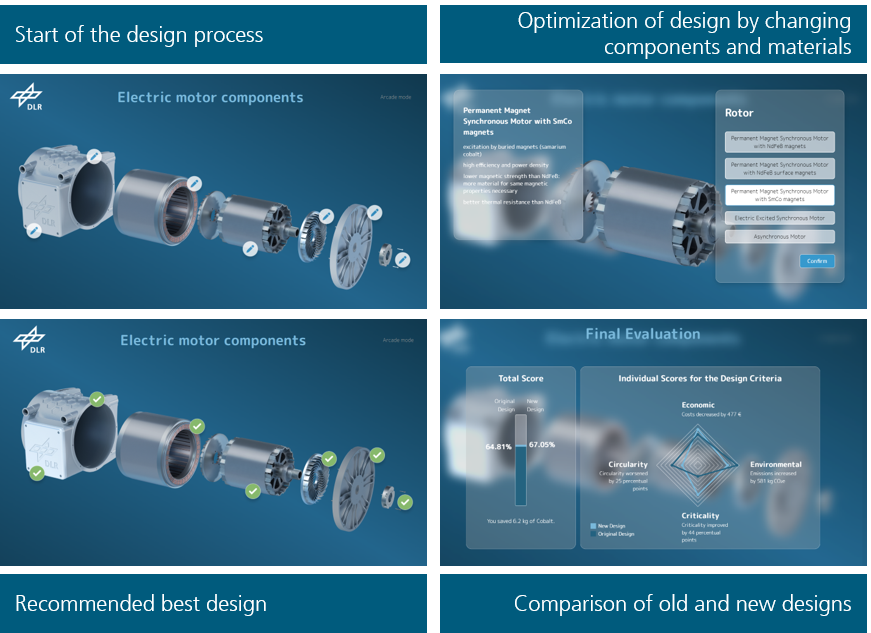
The Design for Circularity Tool is still under development, but can already be tried out as an exhibit at DLR trade fairs and events; most recently in July 2025 at SPACEBUZZ ONE Week in Jena. It shows an electric motor whose components and materials can be made more sustainable by visitors based on the newly developed Design for Circularity methodology. This allows a total of four important criteria to be minimized in order to plan the electric motor of the future: CO2 emissions, recyclability, costs, and criticality (quantity of supply-critical elements, such as rare earths). The real Design for Circularity tool will be developed by the end of 2025. It will then be put into practice in collaboration with industry partners to support product developers in making sustainable design decisions so that products become more recyclable and durable in the future and their production is less susceptible to supply shortages.
Projectfacts:
Duration: | 01/2023 to 12/2025 |
Consortium: | 13 DLR institutes from the fields of aerospace, energy, and transportation |
Scope: | 580 person-months |