From air taxis to passenger jets, many aircraft are equipped with fans. The fans of future engines will have to be much quieter than today's, so the causes of noise generation have to be analysed and understood much more precisely than before. Modern test rigs such as the CRAFT (Co/Contra-Rotating Acoustic Fan Test Rig) make an important contribution to the testing of new propulsion concepts at the prototype stage and to the testing of innovative approaches to noise reduction.
The CRAFT test facility in Berlin is being used to develop future propulsion systems for sustainable aviation. The aim is to minimise noise, which is particularly annoying to people, while maintaining the efficiency of the engines. The results of the tests will provide information on how best to integrate the engines into future aircraft concepts.

Features of the CRAFT test facility
- Detailed investigation of fan sound excitation
- Modular and flexible test set-up: A twin-shaft system allows investigation of both the widely used rotor-stator configurations, as well as aerodynamically efficient rotor-rotor configurations and two-stage compressors.
- Simple replacement of stator blades: Thanks to the numerous test variations and cost-effective test bench operation, the physical sound generation mechanisms can be analysed and characterised using measurement technology to an extent that was previously not possible.
- Inflow control device at the inlet nozzle: This ensures a much more uniform flow in the inlet, allowing undisturbed evaluation of aerodynamic noise sources.
- Installation of sensors and actuators: Aerodynamic probes are used to analyse the stationary and turbulent flow components in the inlet, between the rotor and stator and downstream of the fan with high spatial and temporal resolution. The sound sources generated at the fan and the sound field emitted at the inlet and outlet are recorded simultaneously by 200 microphones and analysed using state-of-the-art analysis methods.
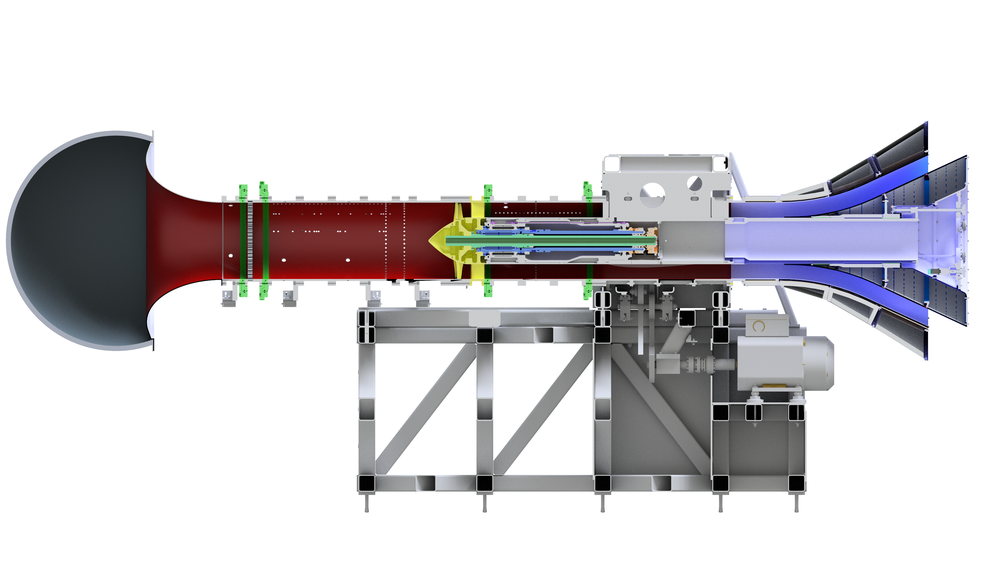
Tecnical Data
Characteristics | Rotor-stator and counter-rotating rotors |
|---|---|
Speed | up to ca. 4500 rpm, adjustable ratio |
Shaft power | 25 kW / 25 kW |
Electrical power | 2 motors with 45 kW each |
Relative blade tip Mach number | 0,33 |
Rotor diameter | 452,4 mm |
Reference rotor-stator stage | |
Rotor number of blades | 18 |
Number of stator blades | 21 |
Mass flow | 7,3 kg/ s |
Pressure ratio | 1,036 |

