Sectional view of the Mole penetrometer
Sectional view of the Mole penetrometer
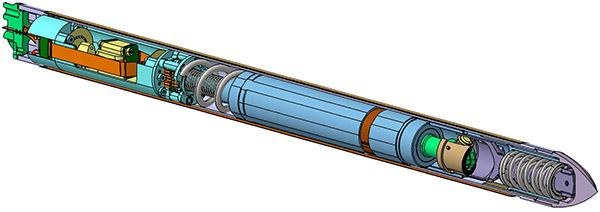
Sectional view of the Mole penetrometer. The electric motor in the centre of the probe (blue) uses a rotating mechanism (green and brown) to tension the main spring near the tip (grey), to which the hammer (purple) is attached. After one rotation, the spring is released and the hammer accelerates forwards, where it then hits the inside of the tip, which acts as an anvil. At the same time, the motor is accelerated backwards. This movement is absorbed by a spring (above the electric motor) and again directed forwards, resulting in a second, weaker blow. The masses and springs are designed in such a way that the probe acts like a mechanical 'diode'. It penetrates the ground as the friction from the walls absorbs the recoil. An tiltmeter and the connection with the temperature measuring cable are located at the top of the probe. Both are protected from mechanical stresses by specially designed damping springs.