Phobos and Deimos together for the first time and in high resolution
Phobos and Deimos together for the first time and in high resolution
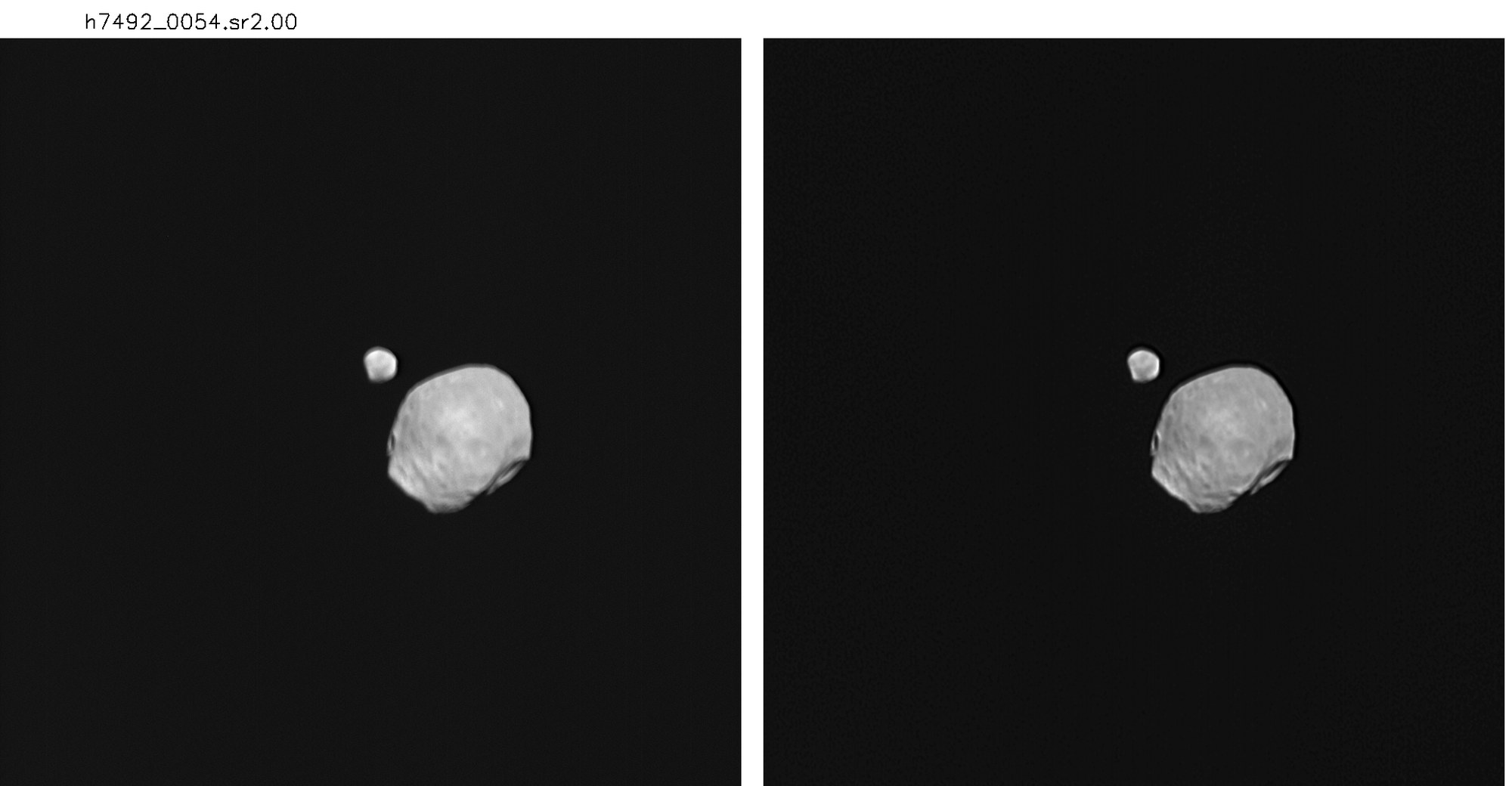
On 5 November 2009 it was, for the first time, possible to acquire images of Phobos and Deimos together in high resolution. A highly precise plan enabled the High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) Experiment Team for Mars Express at the DLR Institute of Planetary Research, in collaboration with the Principal Investigator’s team at the Free University of Berlin, to take a total of 130 images of this unusual configuration.
At the time of the exposures, Phobos, the larger of the two moons (to the right in the images), was 11,800 kilometres away from the Mars Express, while Deimos was 26,200 kilometres away from the camera. Due to these large distances, the Super Resolution Channel of the HRSC was used, a channel that uses an additional lens which, with its field of view of just 0.5°, provides four times the magnification of the HRSC itself. However, the raw images have a small triple-focus error due to the distortion of HRSC’s mirror. The SRC images therefore had to be processed (left-hand image), thus eliminating the unsharpness in the images almost completely (right-hand image). The resolution of the SRC images was around 110 metres per pixel for Phobos and 240 metres per pixel for Deimos, which was twice as far from the camera.